AGRICULTURE & ACCOMODATION
INTERNATIONAL CITY, NEIGHBOURHOOD AND PRIVATE SCALE OF USE.
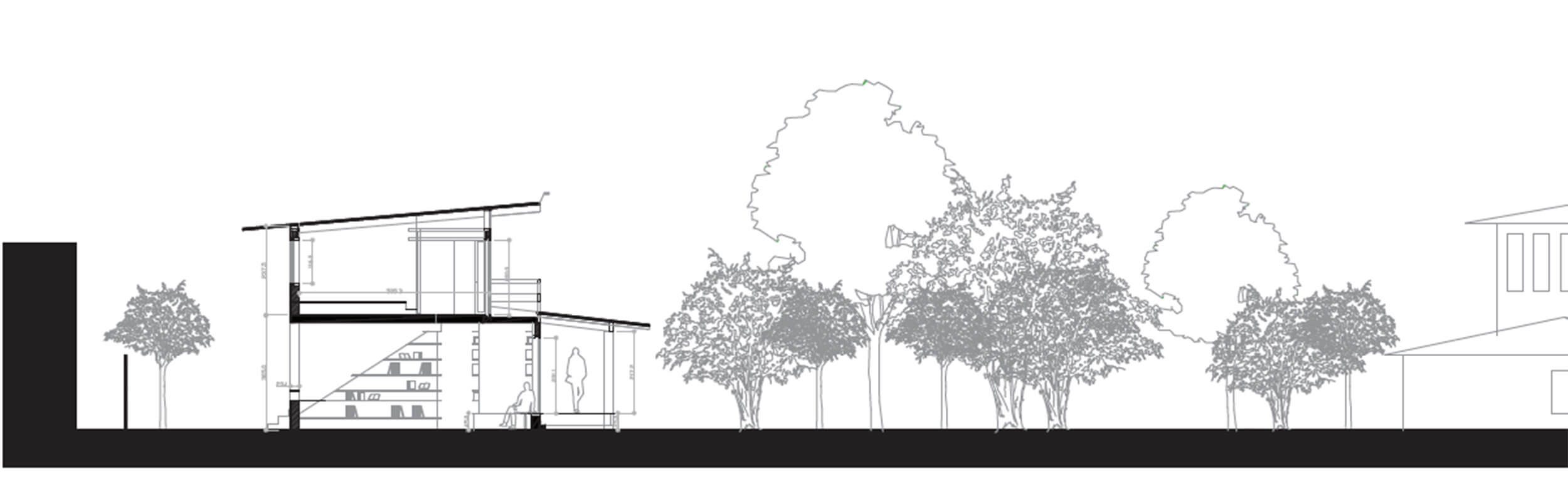
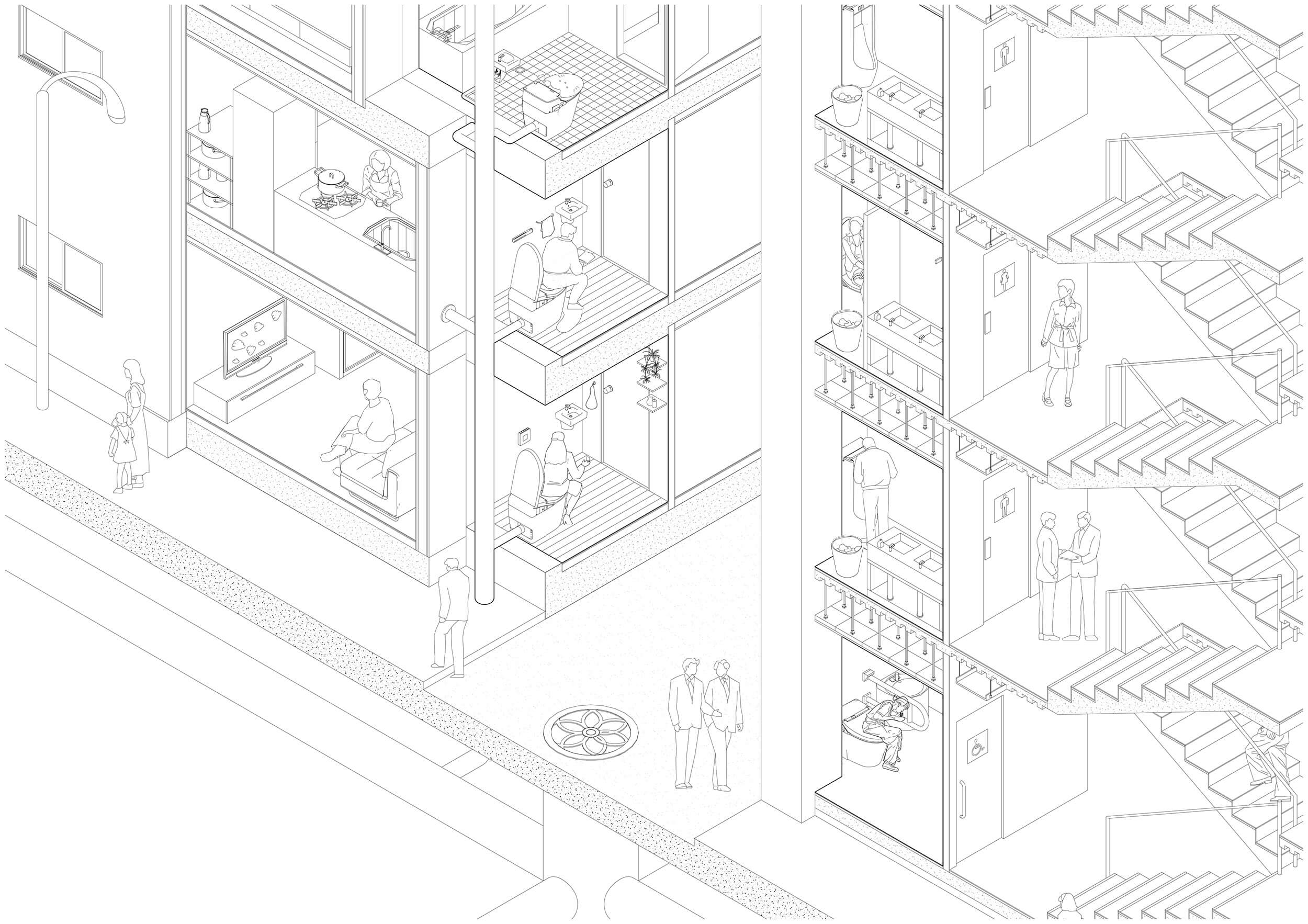
In this project we tried to re-incorpsed agrar- ian past of jiyugaoka into a smaller scale, In order to maintain this strong identity related to activities that habited the area from the begin- ing first through fields and farming and later through an important greenhouse activity.
To make such activities work economicaly and materially it would have to be opened to a certain amount of public, serving the global scale with accomodations, and the neighbour- hood with facilities open to local living people through a membership with an association.
This project has been conducted during the workshop held in collaboration by Tsukamo- to Yoshiharu and Andrea Matin. After the last correction, the group wished to develop fur- ther after the professors critics.
Student: Malou Mamaty
Toilet
The development of the toilet and the treatment of excrement in Japan are closely linked to a growing mechanization of the lavatory as a device and its progressive shift vis-à-vis the house from outdoors to indoors. In the Edo and early Meji Periods toilets were located at the edge of or outside the house. Conceived as a squat-latrine system, made out of wood, it was adapted for the easy collection of the excrement, which was then used as fertilizer. Between the World Wars, new systems, new materials, and even new toilets (for instance toilet bowls) were slowly introduced, while the collection of sewage became more and more mechanized, with basket collection being successively replaced by trucks, then mobile vacuum-extraction units, and later still by a Western type of sewage system with pipes. In recent years the predominant European-based device has become hyper-Japanized, highly automated (including washing, drying, background noise, cleaning, disinfecting, etc.), and even described and praised as something kawaii (cute, adorable) in the public narrative.
Rice Cooker
Rice cooking is an essential part of Japan’s kitchen culture. More than other devices, the rice cooker illustrates its own transformation through technology. In the traditional Japanese household, cooking took place in the kamado, a kitchen space at the entrance with a fixed stove fueled by charcoal. By contrast, today’s rice cooker condenses the functions of energy provision, heating, cooking, and smoke extraction in one single technical device, transforming rice cooking into a more rapid, convenient, clean, and less space-demanding activity. The modern rice cooker is small, lightweight, portable, and easily replaceable, yet as opposed to the kamado it is also deterministic and monofunctional, challenging our understanding of what kitchen culture might be.