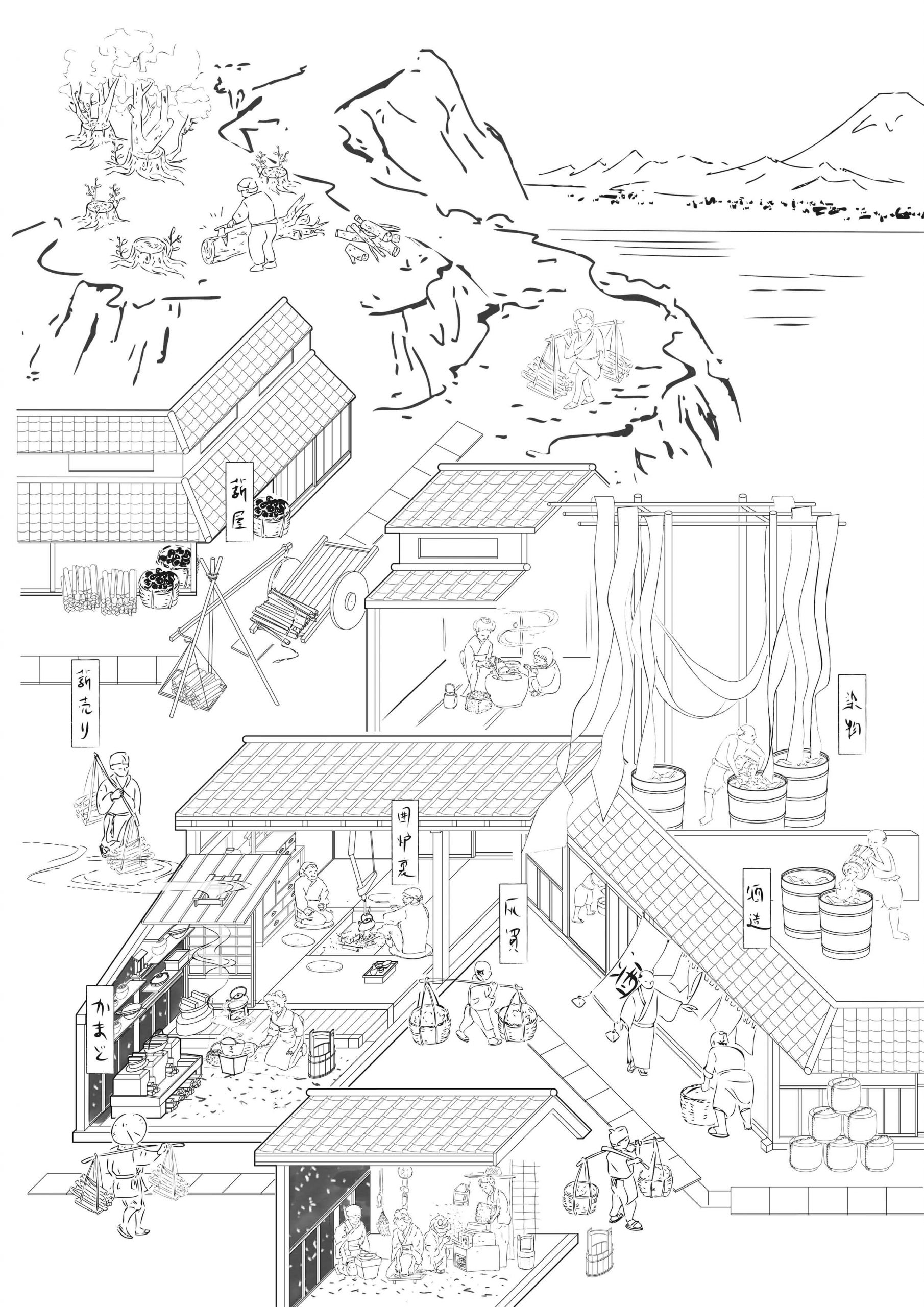
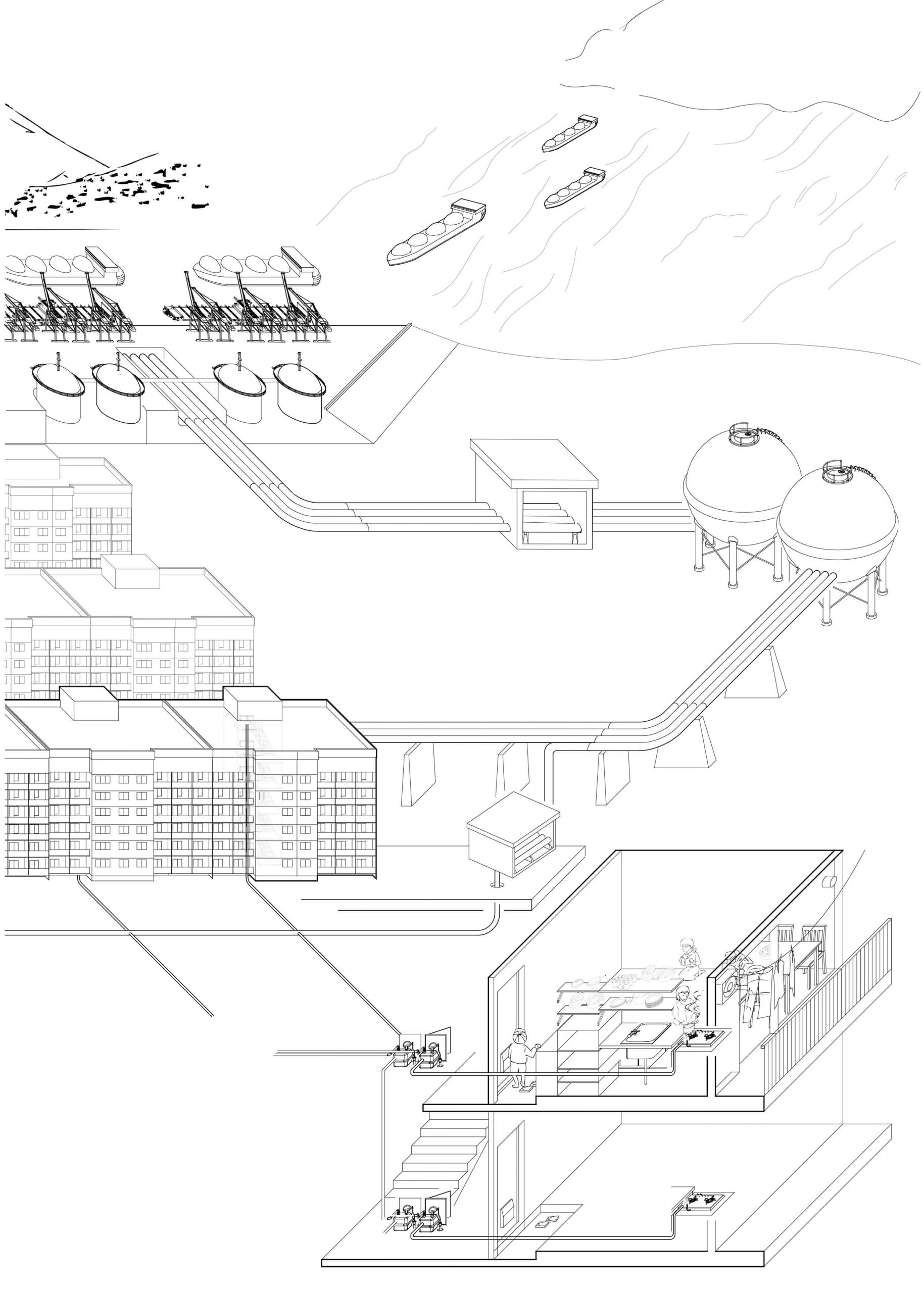
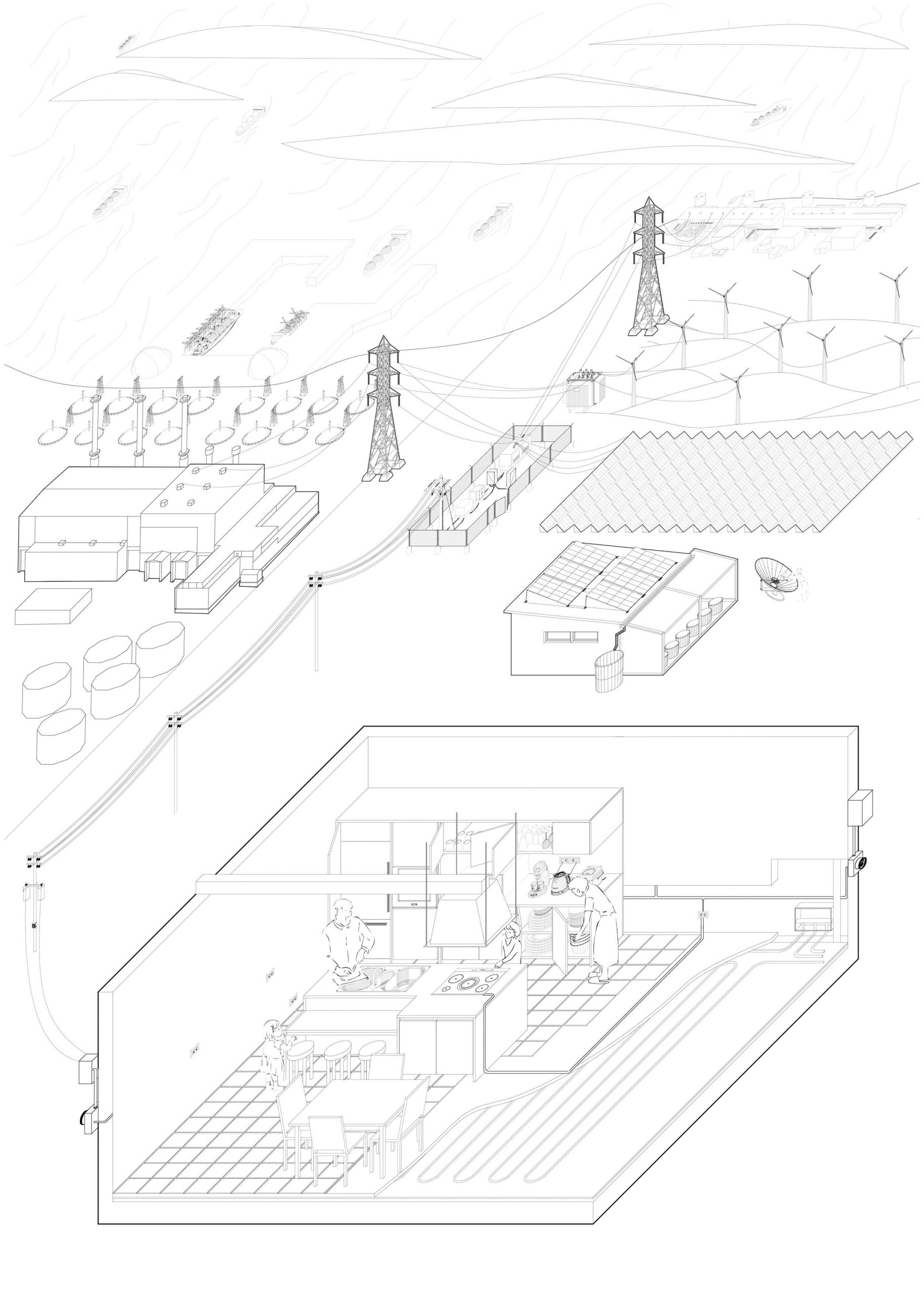
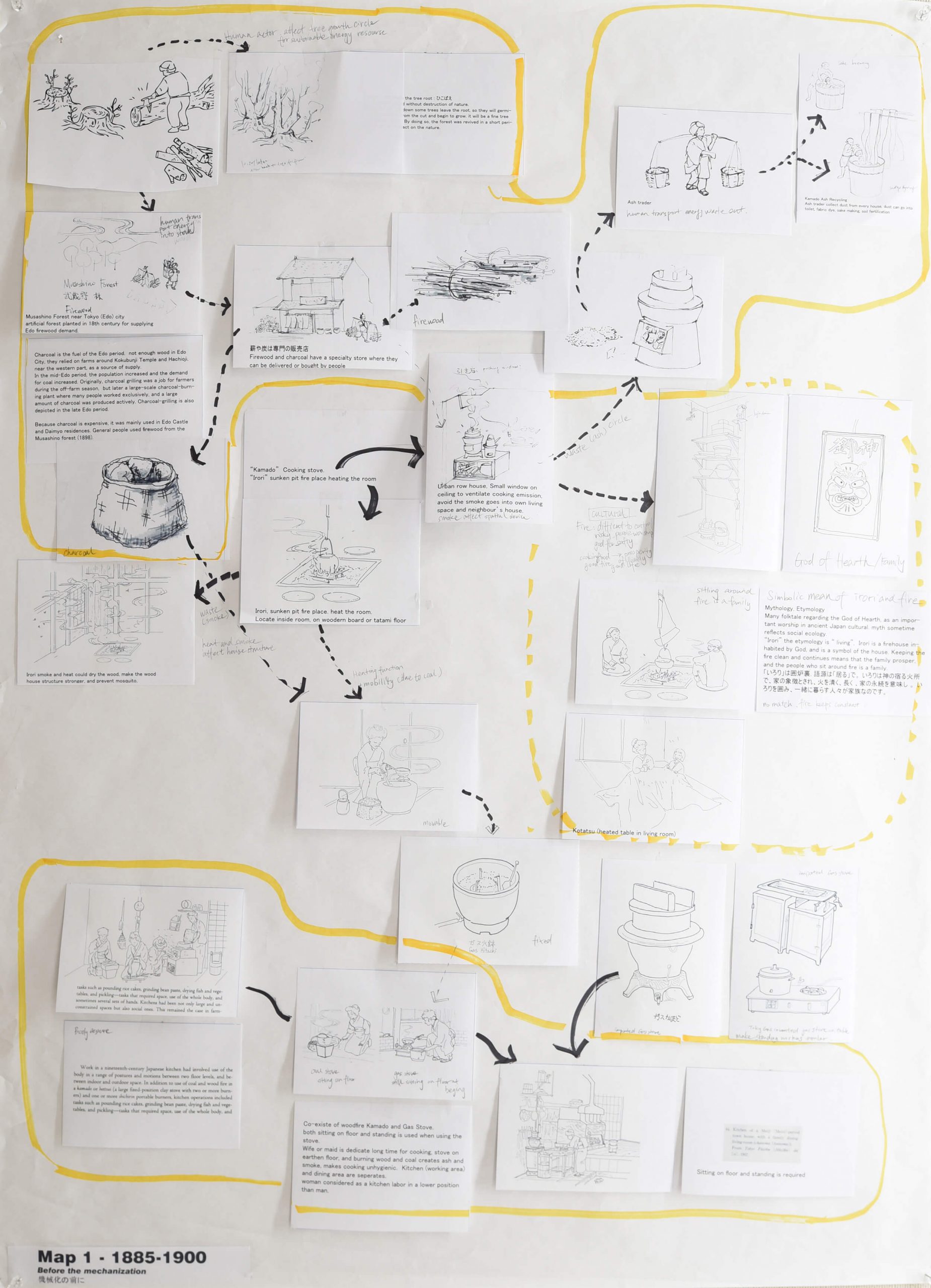
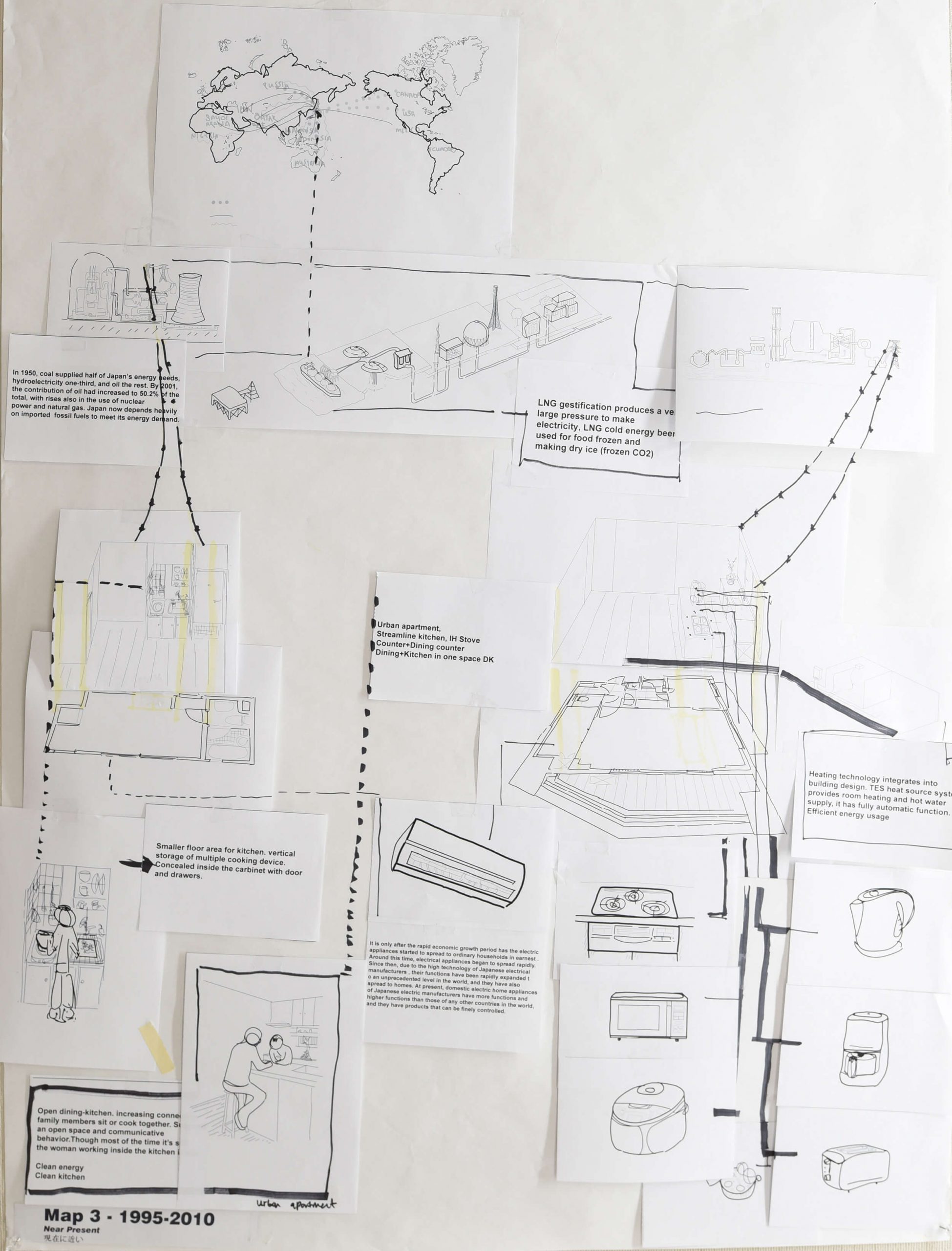
As a once archetypal household element, the stove has gradually become invisible in contemporary housing, with open-flame cooking disappearing into glasstop IH stoves and heating being concealed in the floors. Simultaneously the energy supply system has grown into an extensive and cohesive global network, at once distant and thus invisible to its end users yet heavily transforming the hinterland. Until the end of the nineteenth century the network was tangible and concrete: firewood was acquired from the forest, purchased by each household and used for the stove, and afterward the ash produced was re-collected by ash-traders for other uses such as sake brewing. From around 1960 Japan increasingly imported liquefied natural gas via tanker ships as an alternative energy supply, requiring a complicated gas-supply infrastructure, along with urban renewal, including shipyards, pipelines, gasometers, etc. Today the power system is a hybrid one, fed from multiple resources, including atomic power and renewable energy, making the network evermore extensive and abstruse.
Stove




Project
Students
Teacher
Class
Type
Year
Stove
Emma XiaoEzgi NalciPeijing Hua
Laurent Stalder
2019_Thing of ModernityThing of Modernity – Mapping the Micro-geography of Everyday Environments
–
2020 4Q