THE NIGHT SPENT WITH ART
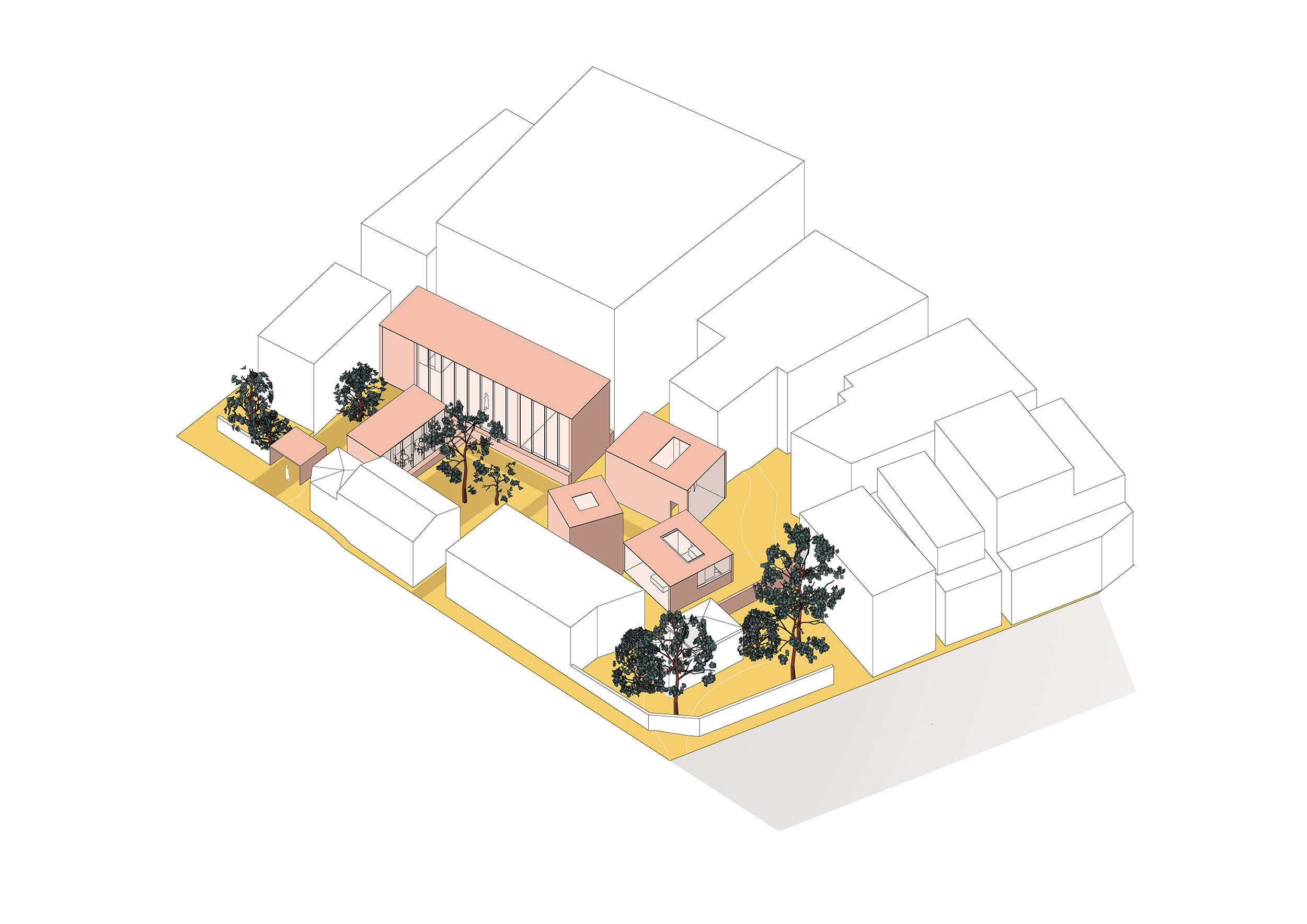
The project is a proposal for an art complex containing an exhibition hall, a visiting artist residence, a café, a sculpture park and three art accomodation units. The site is a parking lot located in a busy area of Jiyugaoka, fac- ing one of the main shopping streets. The part facing the main road is occupied by an old tra- ditional wooden japanese house accompanied by big old trees which are `hiding` the inner part of the site where accomodations are lo- cated and create a quiet lagoon in the middle of this busy district.
The main concept of the proposal is to high- light the cultural history of Jiyugaoka and al- low visitors to experience art from a different perspective, that is to say the opportunity to spend the night together with art.
The artist residence connected to the exhibi- tion hall provides a special experience where the artist can be seen working at the time of ongoing exhibition.
During the day, the accomodations are open to the public as part of the sculpture park. During the night the units, designed to have their own private `gardens` transforms from
exhibition units to accomodating ones.
This transformation was one of the main focus points during the design process of the pro- posal.
The location of the site, disposition of the units on site in a sequence gradually opening up and the fact of unexpected usage of these units re- flects the head theme of unpredictability.
Student: Chiara Tassinari
Genkan
From the Meji Period to today the genkan (a Japanese house-entry-cum-doormat) has evolved from a space of etiquette to a functionalistic space, and nowadays to a space of convenience. In the Meji Period a representative house had three entrances with a front genkan (表玄関), an inner genkan (内玄関), and a katteguchi (an outside connecting door) in the kitchen, reflecting the different social statuses of the master, family members, and servants. Etiquette required a long spatial sequence from the main entrance to the reception rooms, carefully designed and staging the best views to the garden. In post-war apartment houses the traditional design of the genkan was simplified to make it a compact space containing various functions such as storage, washing, receiving goods, or making phone calls. In essence it is designed as a public space inside an apartment. However, in contemporary high-rise residential buildings the boundary between the private interior and the public exterior has been overly stretched by the introduction of common entrance lobbies where guests can be welcomed on the ground floor. Moreover, a series of technical devices, such as cameras, sensors, automatic doors, elevators, and intercoms, have been introduced for security, accessibility, and comfort, again physically lengthening the distance to the private door to an even greater extent.
Elevator
Usually, elevators are supposed to smoothen vertical transportation inside a building. Perfectly integrated into the layout of contemporary office buildings and towers, as well as into the habits of the users, its presence only becomes palpable when the movement of the elevator is disrupted, when the cabin gets stuck, a button does not react, or when the doors do not work as commanded. One of the most common of these frustrated expectations is the sudden closing of the doors of the elevator directly in front of the user—be it by inadvertence, late arrival, or by the deliberate actions of a person inside the cabin—thus deflecting the user from a trajectory that was until that moment taken for granted, and yet simultaneously turning it into a new opportunity.